A recent report by Tennessee-based carbon solutions platform Clearloop noted that private companies have contracted for 71 GW of new renewable energy capacity in the U.S. since 2014, which is enough electricity to power nearly 15 million homes. However, the distribution of solar and wind projects tends to cluster regionally, and not only because of the availability of wind and solar resources. State and utility renewable energy policies play a huge role in where new projects are sited.
Clearloop, which is a subsidiary of solar power producer Silicon Ranch, partnered with non-profit emissions data analysis firm WattTime to study how renewable energy projects – and solar in particular – could be sited to produce better environmental and even social outcomes. The resulting white paper, Curing Carbon Blindness, reinforces the important role of private sector action in growing renewable energy in the U.S. while at the same time saying such action can be better focused to achieve decarbonization goals.
By incorporating the principle of “emmissionality,” the report suggests, companies looking to purchase renewable energy credits (RECs) or offset to their carbon footprints should seek to contract with solar and wind projects in regions with the highest percentage of fossil fuel generation.
Under the current structure, all RECs are essentially created equal, meaning an offtaker in one part of the country can buy RECs from a project anywhere else. There are differences in regional markets, such as ERCOT, but this is generally how it works. Laura Zapata, co-founder and CEO of Clearloop and one of the authors of the carbon blindness report, said not all MWh of clean energy are created equal in terms of their environmental impact.
“We still get over 60% of our electricity in this country from fossil fuels,” Zapata told pv magazine USA. “And so, our goal is how do we build more solar projects in the most carbon intense communities, which also happen to be often the most underserved and disadvantaged communities.”
Unlike most countries, the U.S. does not have a single national energy grid. It is more like a continent with many regional grids of widely varying emissions characteristics. Some regions, such as California, have grids with high percentages of renewables, while others, such as in the southern Appalachians, have fossil-fuel-heavy generation.
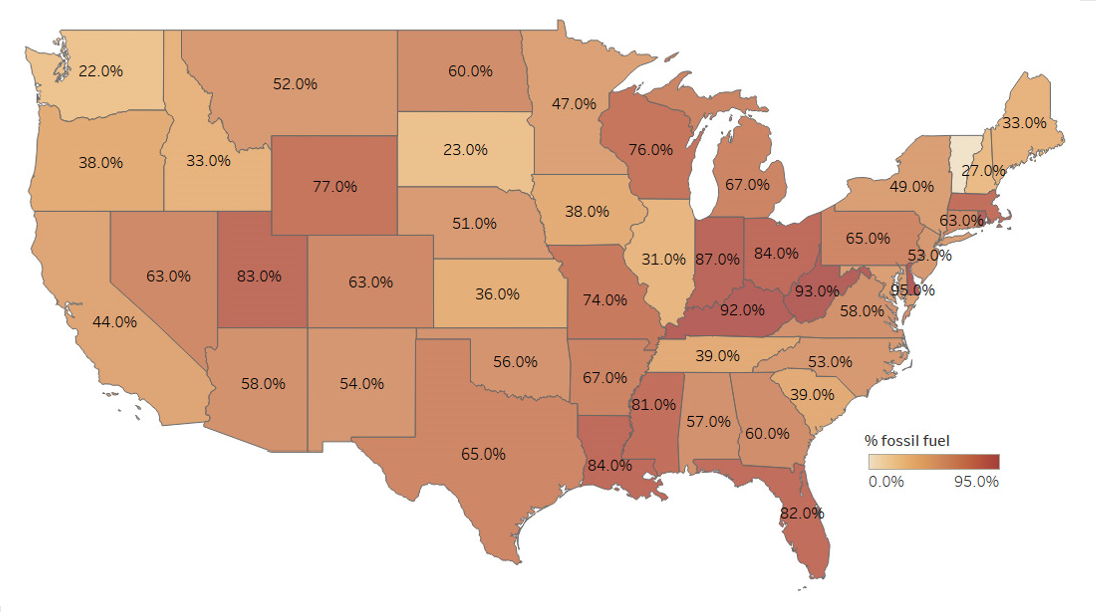
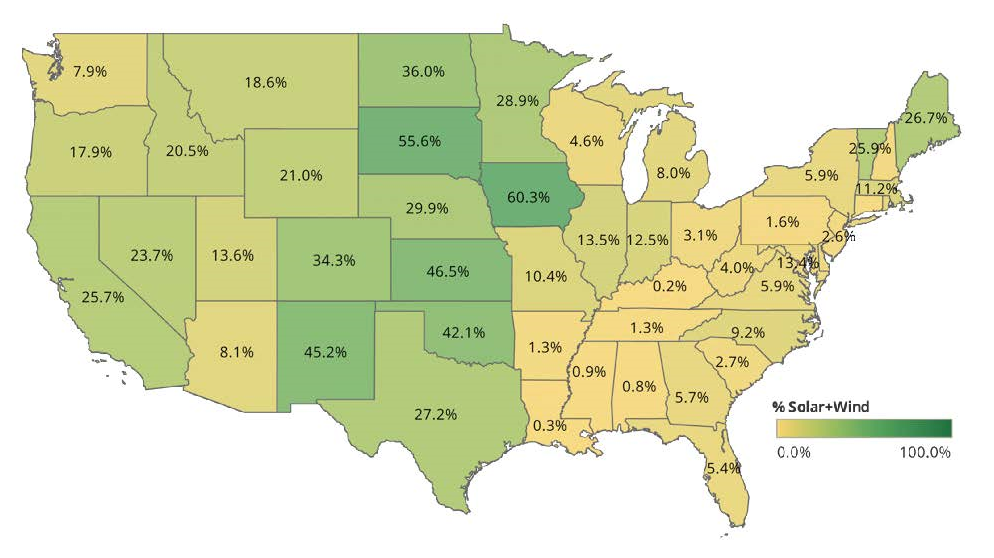
According to the Clearloop report, turning on a light switch in eastern Kentucky will result in 54% more carbon emissions than turning on a corresponding light in Los Angeles. This same data show that a new solar plant located in eastern Kentucky will reduce emissions by 62% more than the same plant would in Los Angeles.
By combining historical irradiance data with WattTime’s marginal emissions data, Clearloop says it is able to model not only how much electricity a solar project is expected to supply the grid, but also the marginal carbon intensity of the power generation sources it is displacing in that region at specific times.
Zapata argues that the marginal difference in emissions that results when solar generation displaces fossil fuel generation should be a key factor in citing projects. Using WattTime’s emissions analysis methodology, Clearloop had identified the regions of the U.S. where new solar, the report’s main focus, would have the greatest decarbonization impact by reducing a like amount of fossil fuel generation sources.
The analysis also extends to voluntary carbon offset markets that rely on private carbon credit registries, such as Verra or Gold Standard. This enables a company to use the methodology for contracting with solar projects to offset its carbon footprint from activities other than electricity consumption, such as air travel.
“Our clients are not interested in the electricity,” Zapata said. “What they want is credit for the environmental impact of those electrons flowing into the grid. So, whether they count them as RECs or offsets, we’re sort of agnostic.”
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.





By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.